[Solved] Consider the diagram depicting the revenue and cost conditions... Course Hero
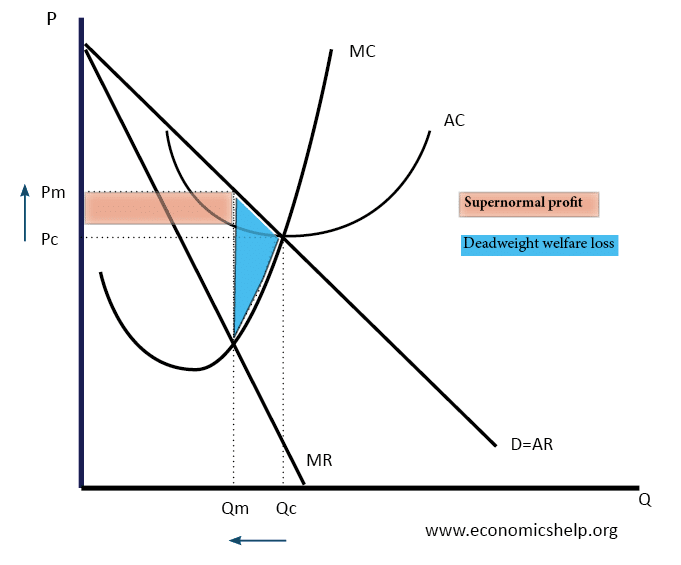
'The' diagram. How price, output and profit is affected by changes in demand (AR) , variable costs and fixed costs
Price, Marginal Cost, Marginal Revenue, Economic Profit, and the Elasticity of Demand
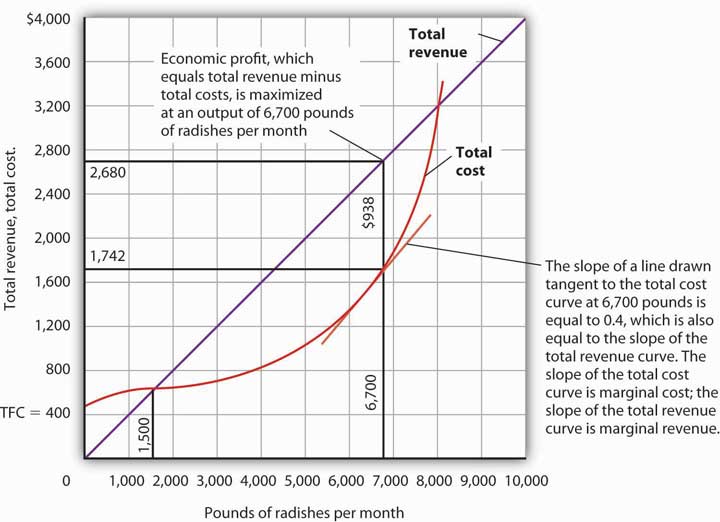
where \(C\) is the total cost. Note we are measuring economic cost, not accounting cost. Since profit is the difference between revenue and cost, the profit functions will be \[π = R − C = $1.2 Q − $40,000.\] Here π is used as the symbol for profit. (The letter P is reserved for use later as a symbol for price.)

What is cost and revenue in economics?, Types of cost, Revenue calculation formula
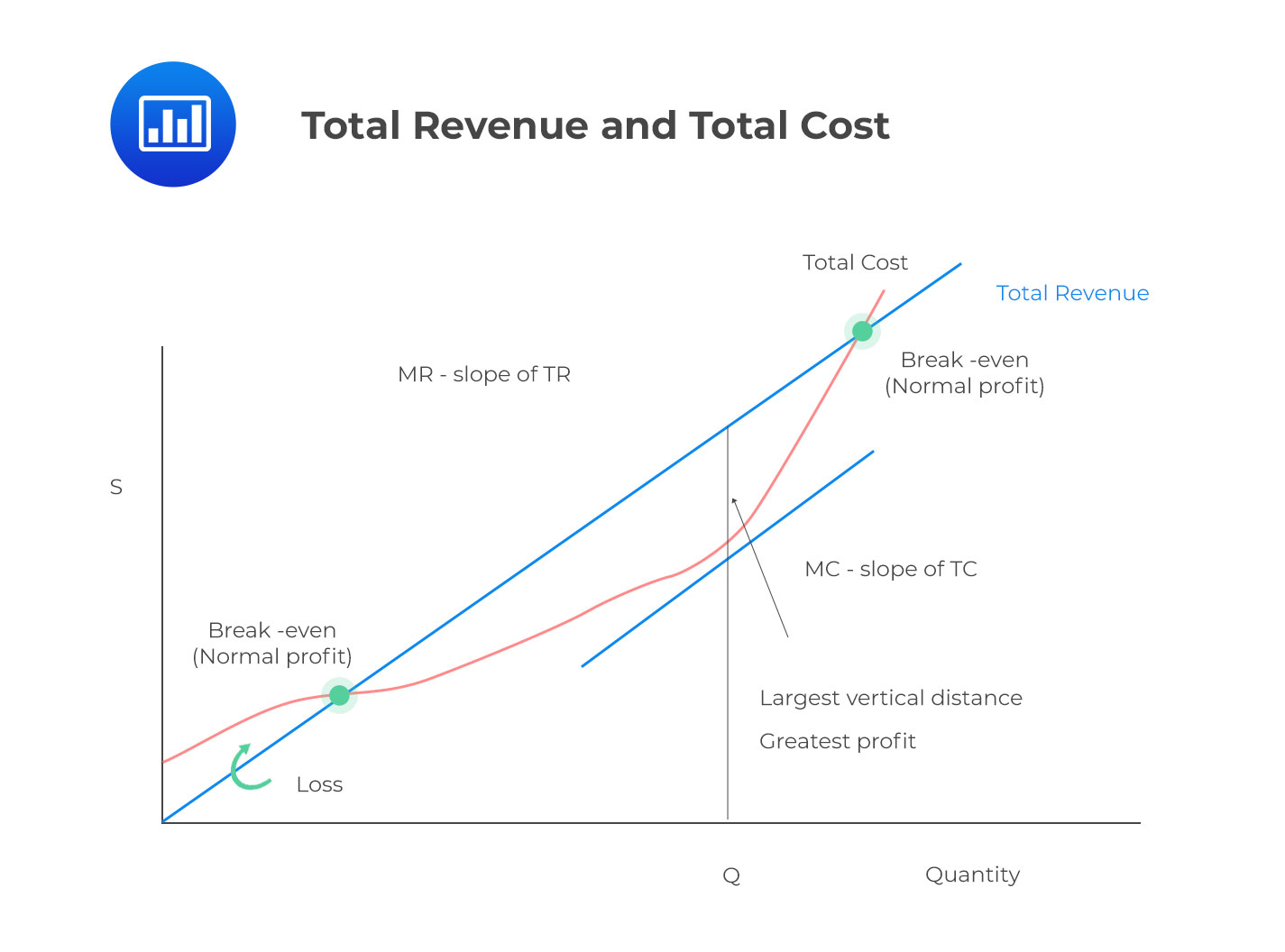
The cost and revenue diagram is an important tool in understanding and explaining how changes in costs (or revenue) can impact a firm's prices, output and profits. In the following example, house-builders face an increase in costs. By manipulating the graph we can identify the likely impact of this on house prices, on the output of new houses.

Revenue — Mr Banks Tuition Tuition Services. Free Revision Materials.
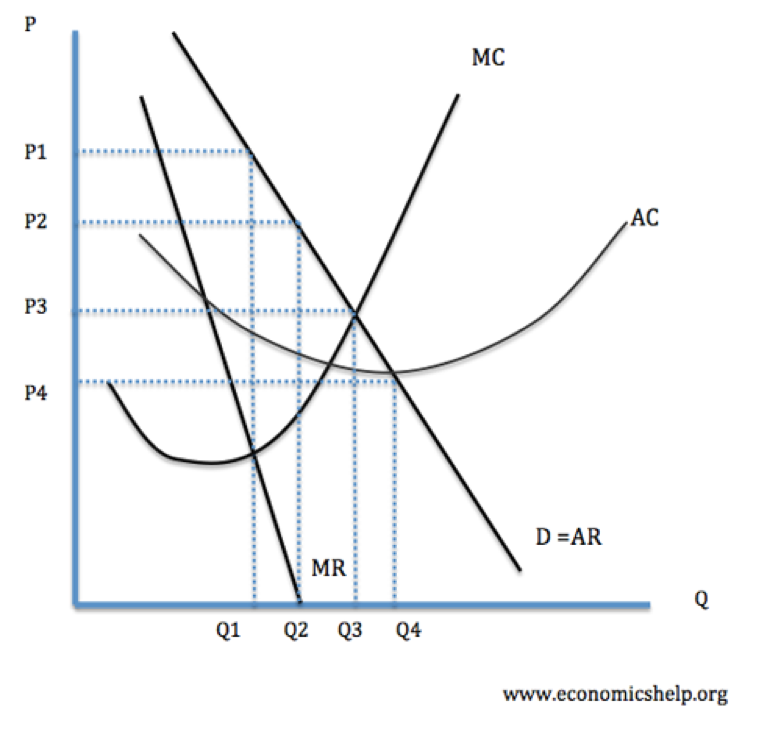
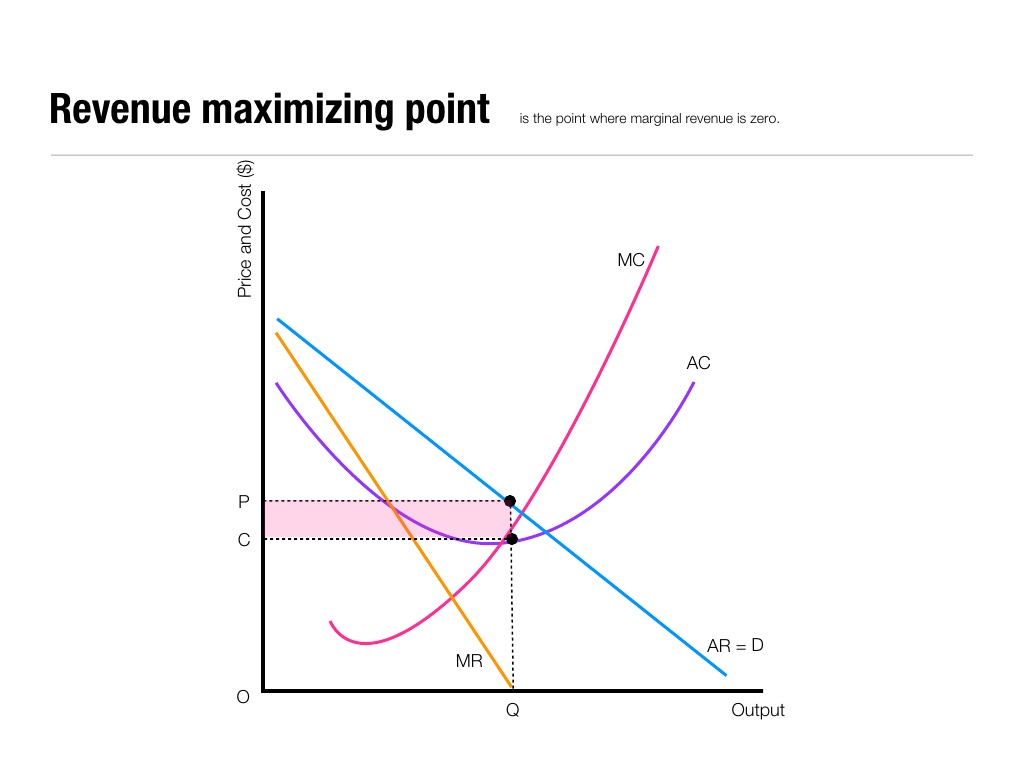
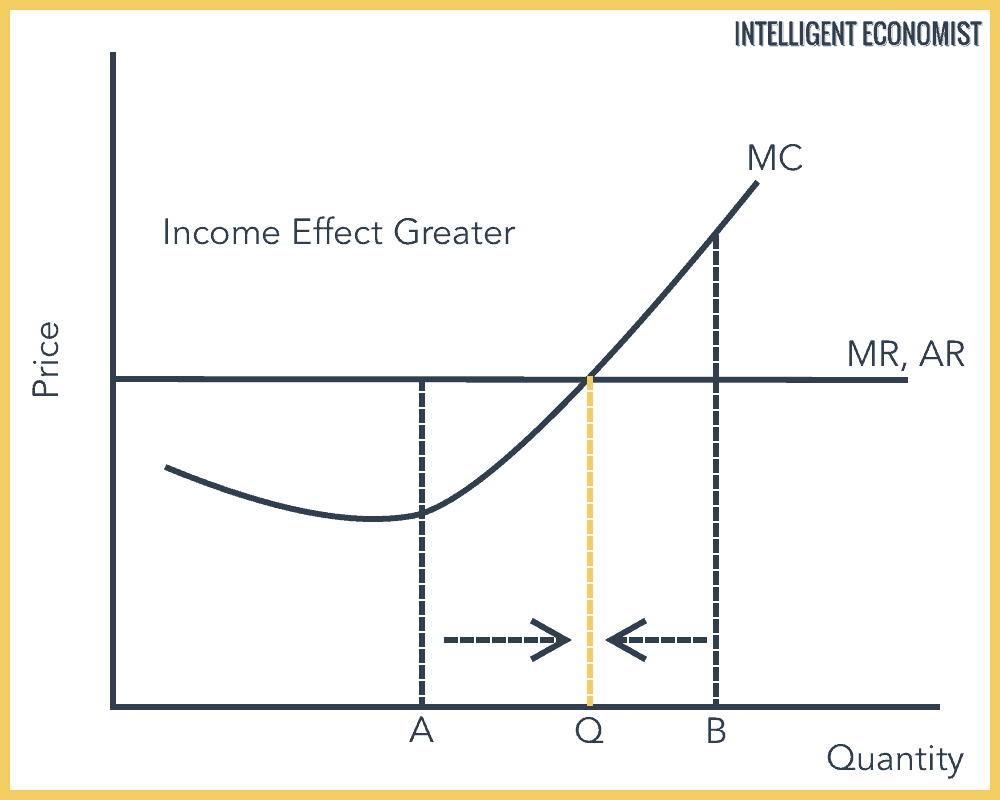
When marginal revenue equals marginal cost, it means that the additional revenue generated from selling 1 more unit (of whatever it is you're selling) exactly offsets the additional cost of producing that 1 unit. In a perfectly competitive market, firms will increase the quantity produced until their marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
RYWitney on Economics Average, marginal and total revenue curves revision diagram
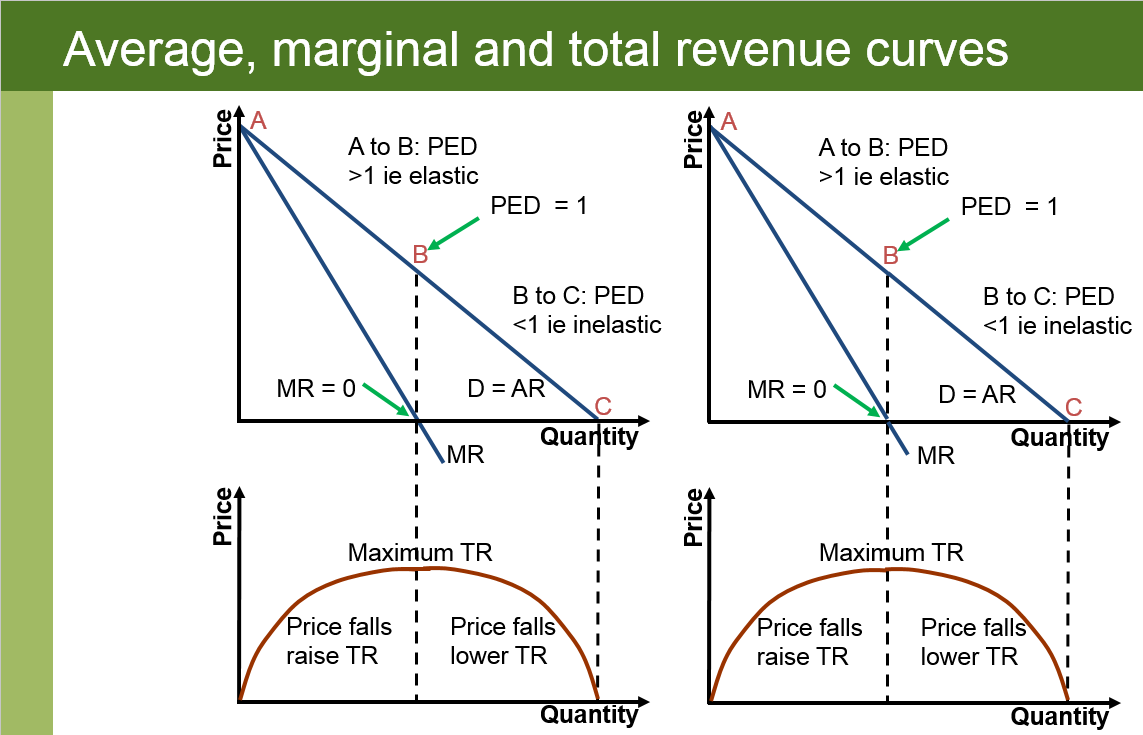
Total revenue is calculated by price x quantity sold. It is the revenue received from the sale of a given level of output. When price is constant, TR is as shown in the diagram. Prices are lowered to achieve higher sales. Marginal revenue: This is the extra revenue a firm earns from the sale of one extra unit.
Output Determination in the Short Run
Students should be able to confidently draw cost and revenue diagrams. This video takes students through a simple step-by-step guide to ensure they pick up f.
Key Diagram Profit, Satisficing, Revenue Economic Investigations
Revenues Notes & Questions (A-Level, IB Economics) Total Revenue (TR) is the total value of sales earnings a firm receives in a given time period. Average Revenue (AR) is the amount of revenue earned by the firm per each unit of output (good/service) sold. Marginal Revenue (MR) is defined as the change (increase) in total revenue by producing.

Business Revenues Economics tutor2u
The revenue would be $1.50 per ice cream bar times 36,000 ice cream bars, or $54,000. The variable cost would be $0.30 per ice cream bar times 36,000 ice cream bars, or $10,800. The fixed cost would be $16,000, making the total cost $26,800. The profit would be $54,000 minus $26,800, or $27,200. Based on this analysis, the students are.
Handout ProfitMaximising Output Economic Investigations
Total Cost (TC) The total cost is the sum of the variable & fixed costs. The total costs cannot be 0 as all firms have some level of fixed costs. Average Fixed Cost (AFC) If the fixed costs of a firm are $1,000 & it produces 1 unit of output, then its AFC is $1,000 ($1,000/1) If the firm increases its output to 1000 units, then the AFC is $1.

Business Revenues Economics tutor2u
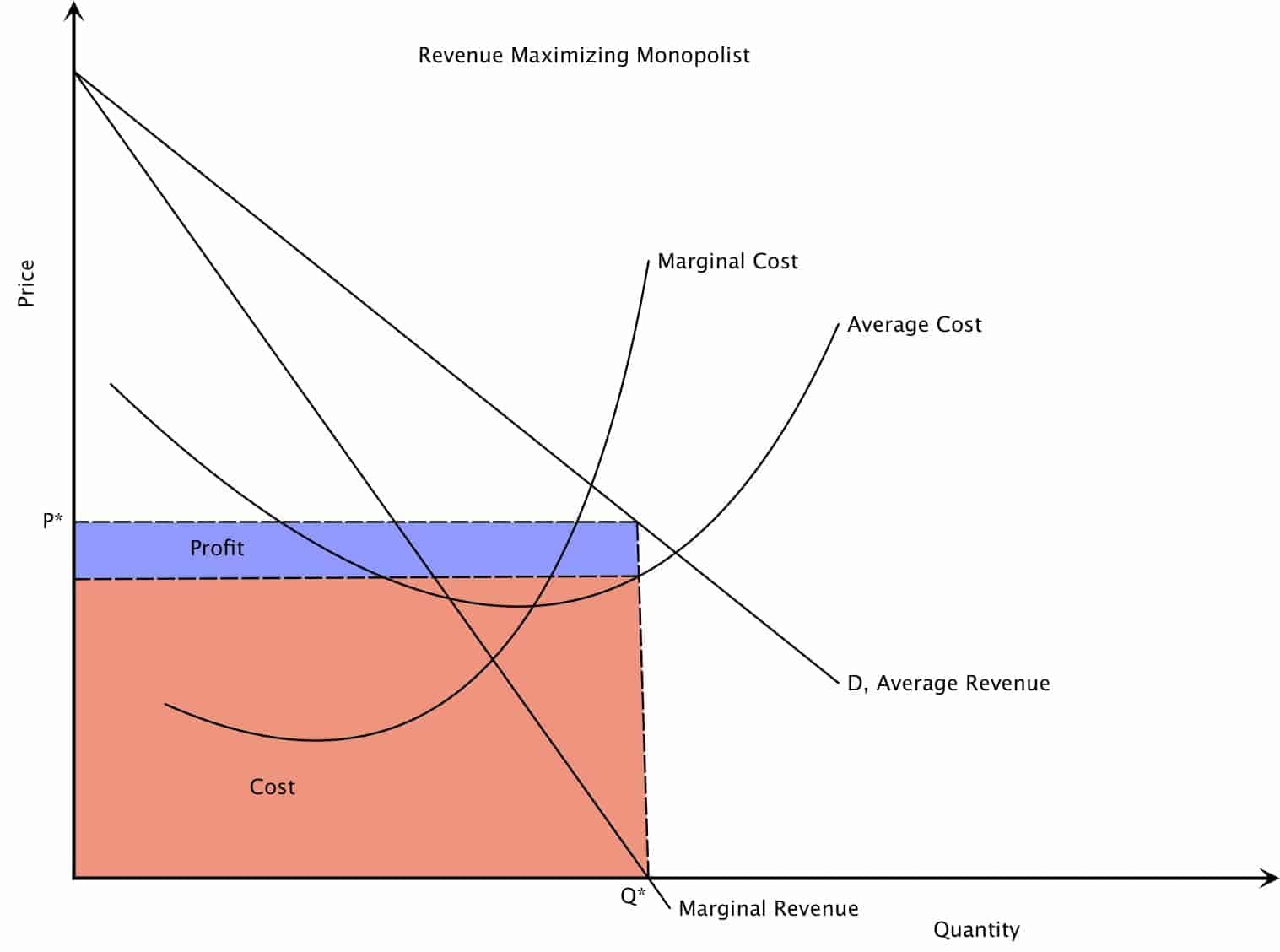
Economics - profit and revenue. 28 November 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger. Total revenue (TR): This is the total income a firm receives. This will equal price × quantity. Average revenue (AR) = TR / Q. Marginal revenue (MR) = the extra revenue gained from selling an extra unit of a good. Profit = Total revenue (TR) - total costs (TC) or (AR.
Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist
How to use the cost and revenue diagram. Profit maximisation.. and average costs fall. However, economic theory predicts that the returns to adding extra variable units of production will begin to diminish - the so-called law of diminishing returns. This drags up average costs and pushes the firm above its productively most efficient level.
The Role of Profit in an Economy
docx, 13.27 KB. A simple step-by-step guide to aid students with the basics of getting to grips with cost and revenue diagrams, one of the more challenging aspects of the Year 2 micro course. Designed by a current Edexcel A Level Economics Expert Examiner. Particularly useful for low ability students who struggle to get to grips with them.

Diminishing returns, cost and revenues, efficiencies, growth of firms Micro Economics Teaching
Technology and production functions, cost minimization and cost curves, profit maximization, comparative statics of output supply and input demands. 2015, and before that worked as the Senior Economist for Aplia, back when all Aplia did was econ. :) I hold a Ph.D. in economics from the University of Pennsylvania, and a B.A. in Humanities.
The Profit Maximization Rule Intelligent Economist
Here are some of the specific things you'll learn to do in this section: Measure variable and total costs as the area under the average variable and average total cost curves. Calculate and graph the firm's average, marginal and total revenues; Measure total revenues as the area under the average revenue curves. Determine the profit.
Oligopoly Diagram Economics Help
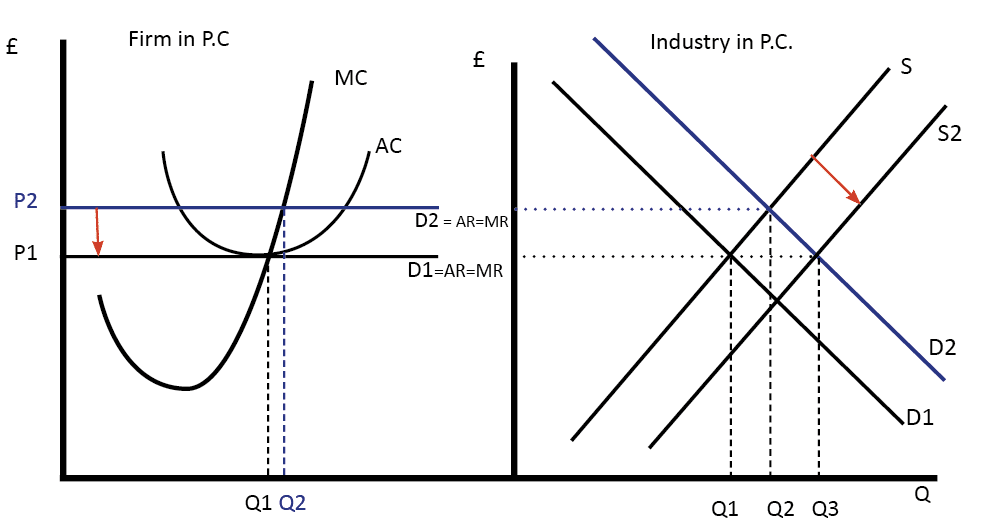
At this price firms make normal profits - because average revenue (AR) = average cost (AC) Changes in Perfect Competition equilibrium . Market demand rises from D1 to D2 causing the price to rise from P1 to P2. Due to the rise in price to P2, profits are now maximised at Q2. A firms marginal cost (MC) curve is effectively its supply curve
Costs and revenue stock image. Image of drawing, lecturer 94368363
Read the question carefully! If it says "using a supply and demand diagram" then you need to use the Year 12 analysis as the basis for your answer. Otherwise consider using cost and revenue curves since this shows that lower costs can lead to higher profits even if the subsidised firm lowers their prices in the market.
- Peter Pan Goes Wrong Nottingham
- Stephen Fry Harry Potter Free
- Recruitment Agency Start Up Costs Uk
- Cross Stitch Kits For Kids
- Teeth Deep Clean Before And After
- Green Wire Mesh Fencing Rolls
- Hoover H Wash 300 Pro Manual
- Diy Village Hall Wedding Decorations
- Old Adidas Predators Football Boots
- Have Yourself A Merry Sheet Music