
Arrest Warrants
Disasters and Emergencies. Know what disasters and hazards could affect your area, how to get emergency alerts , and where you would go if you and your family need to evacuate. Make sure your family has a plan and practices it often. Download the FEMA App to get preparedness strategies, real-time weather and emergency alerts.

What is the difference between a hazard and a risk?
What is Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment? Hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA) are two processes necessary for maintaining a high level of safety and efficiency in the workplace. These processes aim to identify potential risks and hazards, assess their severity, and put management teams in a better position to put controls.

Pin on smart thoughts
Most of OSHA's PELs for Shipyard Employment are contained in 1915.1000 - Toxic and Hazardous Substances, and are listed by chemical name. Most of OSHA's PELs for Construction are contained in 1926.55 - Gases, Vapors, Fumes, Dusts, and Mists, and are listed by chemical name. However, many of these limits are outdated.

hazard identification and risk assessment case study
An employee has a basic incentive to do the least amount of work for the same amount of pay. It benefits the employer to cut down on this moral hazard. The employer may establish incentives that.

Caution Burn hazard,Hot surface,Do not touch Symbol Sign Isolate on White Background,Vector
Hazardous materials can include explosives, flammable and combustible substances, poisons and radioactive materials. Chemical agents are poisonous vapors, aerosols, liquids and solids that have toxic effects on people, animals or plants. Emergencies can happen during the production, storage, transportation, use or disposal of hazardous materials.

Hazards vs Risks What’s the Difference? Reid Middleton
Injury and Illness Prevention. Inspect glassware for defects or cracks before use. Do not handle broken glass with bare hands. Use appropriate cut-resistant gloves to handle broken glass. Use forceps, tongs, scoops, or other mechanical devices for removing or retrieving broken glass from the work area or a fume hood.

When you see a hazard, always report it asap! Health and safety poster, Safety posters
Keep all hazardous materials stored properly. Keep chemicals in dry, cool and ventilated areas, and separate incompatible materials. Always keep lids closed - meaning leak-proof and vapor-tight - on all hazmat containers. Make sure these storage areas are free from items that might cause trips, falls or spills, and free from materials that.

Hazard Communication to Ensure Your Safety The Safegard Group, Inc.The Safegard Group, Inc.
Rule #6. Use all materials solely for their intended purpose. Don't, for example, use solvents to clean your hands, or gasoline to wipe down equipment. Rule #7. Never eat or drink while handling any materials, and if your hands are contaminated, don't use cosmetics or handle contact lenses. Rule #8.

Looking at Workplace Hazards Contendo
Handle, store, and get rid of hazardous materials safely and according to approved procedures. Never pour them down sewers or drains. Don't mix or combine hazardous materials unless you know you can do so safely. Many products can cause violent reactions or release poisonous fumes when combined. Transferring flammable liquids like gasoline.

Hazardous Chemicals 5 Step Guide To Handle Them GoContractor
What should you do when dealing with this hazard? Question topic: Car , Vehicle handling. Favourite. View favourites. A: Switch on your hazard warning lights. B: Use a low gear and drive slowly. C: Use a high gear to prevent wheelspin. D: Switch on your windscreen wipers.

5 Common Workplace Safety Hazards Bernstein Crisis Management
Mark one answer. Switch on your windscreen wipers. Use a low gear and drive slowly. Switch on your hazard warning lights. Use a high gear to prevent wheelspin. View Hint. Check Answer. ← Why is it bad technique to coast when driving downhill? It's a very windy day and you're about to overtake a cyclist.

Reference Guide to GHS Hierarchy UArizona Research, Innovation & Impact
Controlling exposures to hazards in the workplace is vital to protecting workers. The hierarchy of controls is a way of determining which actions will best control exposures. The hierarchy of controls has five levels of actions to reduce or remove hazards. The preferred order of action based on general effectiveness is: Elimination. Substitution.

It doesn't erase their crime but why should you do the time. Let Go of resentment. Quotes
Consider hazards associated with emergency or nonroutine situations. Determine the severity and likelihood of incidents that could result for each hazard identified, and use this information to prioritize corrective actions. Some hazards, such as housekeeping and tripping hazards, can and should be fixed as they are found.

Do's & Don'ts of Dealing with a Difficult Coworker Breakaway Staffing
The safe handling of chemicals in the workplace is a complicated endeavor. The precautions for avoiding chemical exposure depend on the chemical, as well as its state, concentration, and usage. That's why OSHA put the Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard into effect. Under the HazCom standard, employers have to inform workers of all hazardous.

You are dealing with a work full of dangerous hazard, and you... Picture Quotes
What should you do when dealing with this hazard? A: Switch on your hazard warning lights. B: Use a low gear and drive slowly. C: Use a high gear to prevent wheelspin. D: Switch on your windscreen wipers. ← Previous question. Next question →. Hint. In normal conditions, a ford can be crossed quite safely by driving through it slowly.
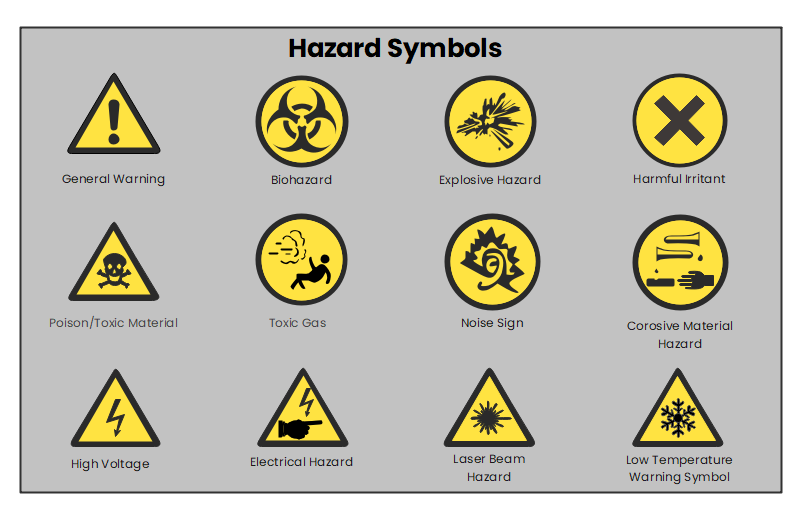
Lab Safety Symbols and Hazard Signs, Meanings EdrawMax Online
Prudent execution of experiments requires not only sound judgment and an accurate assessment of the risks involved in the laboratory, but also the selection of appropriate work practices to reduce risk and protect the health and safety of trained laboratory personnel as well as the public and the environment. Chapter 4 provides specific guidelines for evaluating the hazards and assessing the.
- Squirrel Pest Control Near Me
- Paradise Beach Club Hotel Sri Lanka
- Dry Ice For Cocktails Uk
- Identifying Old Lead Bullets Uk
- Volvo 1800es For Sale Uk
- Man Tge 4x4 Camper For Sale Uk
- Circuit Of Ireland Rally 2023 Route
- Indesit Washer Dryer All Lights Flashing
- M 2 Ngff Ssd To 2 5 In Sata Adapter Converter
- Large Winnie The Pooh Teddy